Consensus Protocol?
At the core of blockchain is the promise of a trustless system where the community is used to verify the validity of transactions. How does it accomplish it? Consensus protocols are the names given to the various approaches used by different networks to verify transactions.
A blockchain network’s core consensus protocol provides a precise way of determining whether a transaction is genuine or false. It offers a way to verify the data that should be included in a blockchains’ record.
Stellar Consensus Protocol?
SCP is an open-source system that offers a unique way to reach consensus without relying on a closed system to record financial transactions accurately. In SCP, there is no requirement of transaction approval from every miner in the network. SCP uses the Federated Byzantine Agreement (FBA) algorithm, which allows for quicker transaction processing, and is said to process up to 1,000 network operations per second.
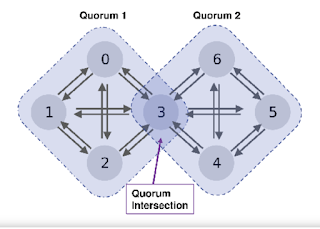
Also, the Stellar Consensus Protocol functions by letting nodes choose other nodes they believe to be reliable and then working with them to produce and validate a set of valid transactions to alter the ledger’s state. These nodes then pick other trustworthy nodes to collaborate with and follow suit to arrive at network consensus through a quorum.
Stellar Consensus Protocol Vs. Proof-of-Stake
The Proof-of-stake consensus mechanism relies on a node’s staking power to validate transactions. Proof-of-stake requires less computational energy to verify blocks and transactions. So, owners offer their coins as collateral for the chance to verify blocks and validate transactions. Validators are then randomly chosen to confirm transactions and validate block data. Owners have to stake a specific amount of coins to become validators. For instance, validators must stake 32 ETH for the chance to become a validator.
This process is totally different from the Stellar Consensus Protocol. As mentioned earlier, SCP is a construction of the Federated Byzantine Agreement (FBA), which differs from the POS and POW mechanisms. FBA relies on the collaboration of trusted nodes.
Each participating Stellar node selects the node they want to trust. This system provides flexibility and decentralized control. Stellar does not offer monetary rewards for validators. Instead, validators understand that they are contributing to the resilience and security of the network.
Stellar Consensus Mechanism Vs Proof-of-Work
The proof-of-work consensus mechanism is one of the oldest in the blockchain ecosystem and is used by the likes of Bitcoin. Ethereum only recently moved to a proof of stake. Proof of work is heavily secure. But, it is energy intensive since it relies on the computational energy of miners.
Under the Proof-of-Work mechanism, miners are block creators. So, miners aim to solve for the hash, which is a cryptographic number, to verify transactions where they receive rewards to do it. Miners, however, need to invest in heavy computing equipment to become block creators. And these often come with heavy energy bills.
The Stellar Consensus Protocol is not energy intensive like the POW. However, proof-of-work has become more popular.
Stellar Consensus Protocol Criticism
The consensus protocol serves as the structure for verifying transactions in the Stellar Network. Participating nodes often have to agree on the rounds of transactions coded into the ledgers of the networks. But this mechanism has faced criticism:
1. The reduction of transaction safety in favor of node integrity and system activity.
2. The ability of the consensus algorithm to attain correctness.
Other consensus mechanisms, including the POW and POS, have their fair share of scrutiny. POW, for instance, is energy-intensive, needing costly equipment to mine. While POS is more eco-friendly, there are concerns it could lead to censorship and decentralization.




Will review your comment and get back!